1. Effect of BioCell Collagen®, on Improving Joint Comfort: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.
- Eighty subjects were divided into two groups and administered either 2 g of BioCell Collagen® supplement or placebo for ten weeks.
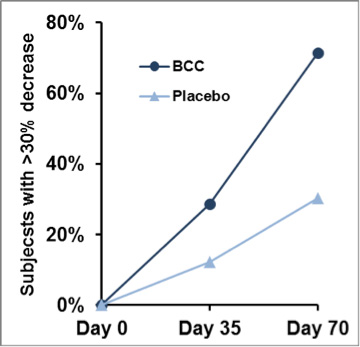
- Compared to placebo, the BioCell group had a significant improvement of joint comfort on days 35 (p = 0.017) and 70 (p < 0.001).
- BioCell group experienced a significant improvement in physical activities compared to the placebo group on days 35 (p = 0.007) and 70 (p < 0.001).
- BioCell Collagen was well tolerated and found to be effective, thereby improving mobility and quality of life.
The peer-reviewed study was published in the Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry. (https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jf205295u) (Schauss et al., 2012).
Results of study – Min. 30% improvement in 71% of subjects taking BioCell Collagen
2. A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Pilot Trial Evaluating the Safety and Efficacy of BioCell Collagen® in Adults for Joint Comfort
- Sixteen subjects split evenly into two groups, ingested 1000 mg of BioCell Collagen® twice daily (2 g) or placebo for eight weeks.
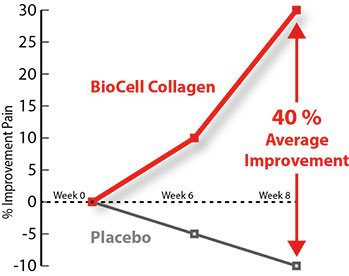
- As compared to the placebo group, the BioCell group showed 40% improvement
- No adverse events associated with BioCell Collagen.
The study details were presented at the international conference of Experimental Biology, 2004, Washington, DC.
Results of the study – 40% improvement
3. BioCell Supplement on Subjective Discomfort (1999)
- This 89 subject, prospective, crossover double-blind clinical study compared 2 g daily supplementation of the BioCell ingredient versus placebo over three months.
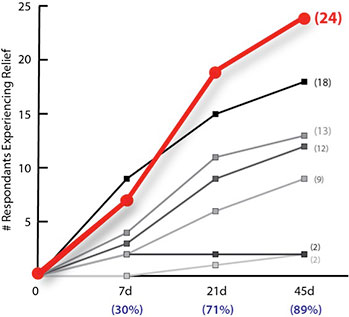
- Out of the 89 participants who complained of subjective discomfort of various types, 80 of them (89%) reported some level of improvement within 45 days of taking the BioCell supplement.
- In contrast, only one subject on placebo had improved.
- No adverse events with the BioCell supplement. (1999 unpublished study)
Results of study – Effective in 89% of subjects
4. Effects of BioCell Collagen® on connective tissue protection and functional recovery from exercise in healthy adults.
- In this pilot study, 3 g of BioCell Collagen supplement daily for six weeks enhanced recovery following weight training exercise and favorably impacted certain bio-markers of tendon and ligament connective tissue.
The study findings were published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition (JISSN): http://www.jissn.com/content/11/S1/P48
